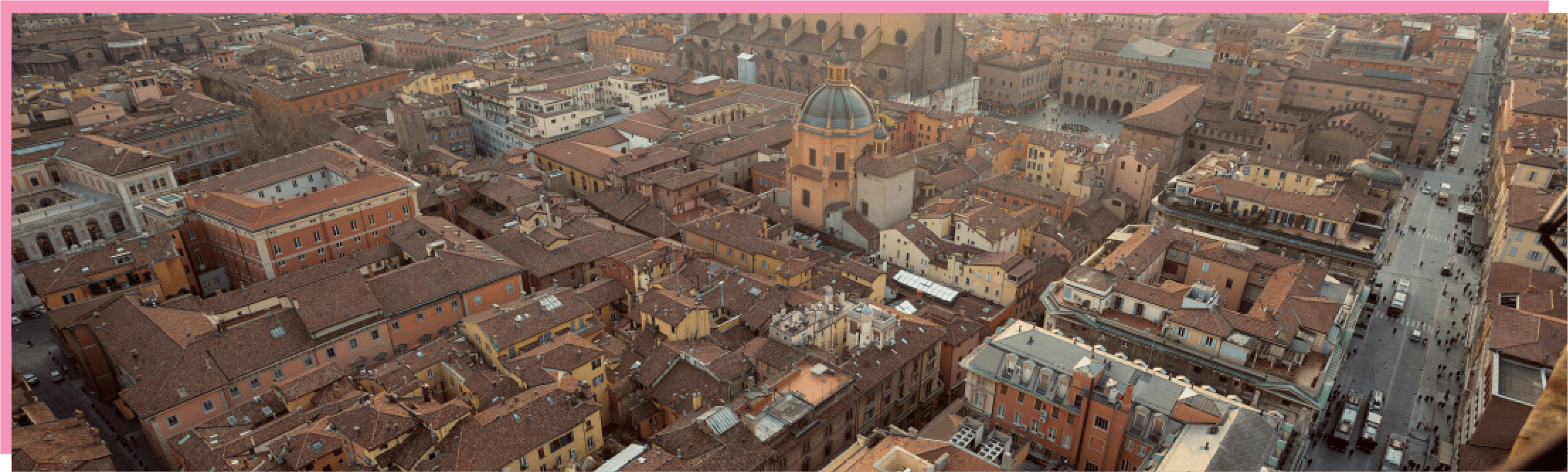
Bologna is the capital city of the Emilia-Romagna region in Italy, at the centre of a metropolitan area of about 1 million inhabitants. Bologna is in the Po Valley, one of the most polluted and densely populated areas in Europe (2700 inhabitants/km2). As of 01/01/2023, Bologna accounts for 387842 residents, of which 52.4 % are females with the highest proportion of the population between 30 and 64 years old.
Climate policies in the city include: Pact for energy and climate, a Climate Adaptation plan since 2015, merged in 2018 with the Action plan for energy and climate, Sustainable Energy Action Plan (SEAP), and Local Adaptation Plan to CC. The Region has approved a Strategy for climate adaptation and mitigation and the Pact for work and Climate in 2021, aligning the Region’s strategy with the UN 2030 Agenda, the Paris Agreement and the EU objectives for CO2 reduction. The Municipality and the Metropolitan City of Bologna are committed to the Global Covenant of Mayors since 2008, and in 2014 the Municipality joined the Covenant initiative on adaptation to CC “Mayors Adapt”. In 2022, the city of Bologna has been included among the 100 cities that will be carbon neutral by 2030.



Bologna, Italy
In Bologna, severe summer heat waves, characterized by high temperature (e.g., >35°C) and humidity, are becoming increasingly frequent. Persistent high pressure, reduced ventilation and clear sky favour high air pollutant concentrations.
Knowledge areas & related content

Bologna is home to the oldest University in the western world (1088 CE). It is famous because of its towers, long porticos – declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2021 – and a well- conserved historical city centre, among the most extended in Italy.

Bologna presents a mid-latitude, four-season humid temperate climate, with very hot and humid summers and cold humid winters. Summer heat waves, often accompanied by drought, are becoming more frequent.
In addition, the low wind intensity together with the stability conditions contributes to the formation of fog and to the persistence of elevated air pollution levels. Altogether, these circumstances might impact adversely health conditions.

Bologna is home to the oldest University in the western world (1088 CE). It is famous because of its towers, long porticos – declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2021 – and a well- conserved historical city centre, among the most extended in Italy.
Bologna presents a mid-latitude, four-season humid temperate climate, with very hot and humid summers and cold humid winters. Summer heat waves, often accompanied by drought, are becoming more frequent.
In addition, the low wind intensity together with the stability conditions contributes to the formation of fog and to the persistence of elevated air pollution levels. Altogether, these circumstances might impact adversely health conditions.

Contact
If you want to know more about the work of the CHC Lab Bologna or want to get involved in the lab please contact:
Prof. Igor Diemberger
Dr. maria Carelli
Dr. Paolo Ruggieri
Dr. Salvatore Pascale
Dr. Erika Brattich


